2025 How to Understand Fluid Power Hydraulics for Beginners and Experts
Fluid power hydraulics is an essential field that encompasses the principles of using fluid to generate, control, and transmit power. With the global fluid power market projected to reach USD 57.5 billion by 2025, the significance of mastering both foundational knowledge and advanced techniques in fluid power hydraulics has never been more crucial. Industry experts emphasize the necessity of adequate training, as improper use or understanding can lead to inefficiencies and safety hazards. According to Dr. Emily Grant, a renowned authority in fluid dynamics, "Mastering fluid power hydraulics is not just about understanding components; it's about creating a synergy between mechanical systems and fluid mechanics."
This comprehensive guide aims to bridge the knowledge gap for both beginners and seasoned professionals in the fluid power hydraulics sector. Through structured sections that highlight key principles, practical applications, and contemporary innovations, readers will gain insights into this dynamic industry. As the role of fluid power hydraulics continues to evolve, staying updated with industry trends and technologies is vital for maximizing efficiency and productivity. Whether you're embarking on your journey in fluid power hydraulics or seeking to enhance your expertise, understanding its core concepts will empower you to excel in your endeavors.
Understanding the Basics of Fluid Power and Hydraulics
Fluid power hydraulics is a pivotal technology utilized across various industries, providing efficient means of transferring energy through fluids. Understanding the basics of fluid power involves grasping the fundamental principles of hydraulics, which operates according to Pascal's principle: when pressure is applied to a confined fluid, it is transmitted in all directions equally. This principle is critical as it underscores the potential of hydraulic systems to lift heavy loads with relative ease and precision. According to industry reports, over 90% of heavy machinery in construction and mining relies on hydraulic power, emphasizing the technology's importance in operational efficiency.
The hydraulic system comprises essential components, including pumps, valves, cylinders, and actuators. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the system operates smoothly and effectively. For example, hydraulic pumps convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, generating fluid flow necessary for operation. Experts note that the global hydraulic equipment market is expected to reach approximately $55 billion by 2025, driven by investments in automation and the rise of smart factory technologies. Understanding these components and their interactions enables beginners and seasoned professionals alike to troubleshoot issues, optimize performance, and innovate within their respective fields, allowing for enhanced productivity and sustainability.
The Key Components of Hydraulic Systems Explained
Hydraulic systems play a crucial role in various industrial applications, where the effective transmission of power through fluid is essential for operational efficiency. At the core of these systems are key components including hydraulic pumps, actuators, valves, and reservoirs. Hydraulic pumps convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, enabling the movement of fluid through the system. According to a report by the International Fluid Power Society, the global hydraulic equipment market is projected to reach $60 billion by 2025, underscoring the significance and growth of this technology in modern industries.
Valves are vital for controlling the flow and pressure within hydraulic systems, ensuring that fluid is directed to the appropriate components as needed. The precise operation of these valves can impact the overall performance and energy efficiency of the system. Actuators, which can be hydraulic cylinders or motors, ultimately convert the hydraulic energy back into mechanical energy to perform work. Research indicates that optimizing the design and efficiency of these hydraulic components can result in energy savings of up to 30%, making them a focal point for engineers striving for both sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
In addition to these components, proper fluid selection and maintenance practices are essential for ensuring longevity and reliability. The hydraulic fluid not only transmits power but also provides lubrication and cooling. With ongoing advancements in fluid technology, data from technical journals suggest that using high-quality hydraulic fluids can enhance performance and reduce wear, further pushing the boundaries of hydraulic system capabilities in various applications.
Common Applications of Hydraulic Power in Various Industries
Hydraulic power plays a critical role in various industries, leveraging the principles of fluid mechanics to perform tasks that would be otherwise inefficient or impossible with mechanical systems alone. A report from the International Hydraulics Association indicated that the global hydraulic equipment market is projected to reach approximately $60 billion by 2025. This growth underscores the increasing reliance on hydraulic systems across sectors such as construction, manufacturing, and automotive production.
In construction, hydraulic power is the backbone of heavy machinery, enabling the operation of equipment like excavators, bulldozers, and cranes. For instance, a study conducted by the Construction Industry Institute revealed that hydraulic systems enhance operational efficiency by up to 30%, allowing for precise control and greater lifting capabilities. Similarly, in the manufacturing sector, hydraulic presses are essential for metal forming and assembly processes, providing consistent force and reliability. According to a market analysis, hydraulic systems account for nearly 40% of manufacturing equipment in North America, highlighting their integral role in shaping the industrial landscape.
The automotive industry also significantly benefits from hydraulic applications, particularly in braking systems and power steering. The Global Hydraulic Braking Systems market is expected to grow by over 5% annually through 2025, driven by the rising demand for safety features in vehicles. Hydraulics not only improve performance but also enhance the reliability of critical systems, making them indispensable in modern vehicle design and manufacturing. The versatility and efficiency of hydraulic power systems position them as a cornerstone of innovation across various industries, reflecting their importance in daily operations and future developments.
2025 How to Understand Fluid Power Hydraulics for Beginners and Experts - Common Applications of Hydraulic Power in Various Industries
| Industry | Common Applications | Hydraulic Equipment Used | Benefits of Hydraulic Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Excavators, Lifts | Hydraulic Pumps, Cylinders | High force, Precision control |
| Manufacturing | Stamping, Forming | Hydraulic Presses, Motors | Efficiency, High output |
| Aerospace | Landing gear operation | Actuators, Valves | Reliability, Lightweight |
| Automotive | Brake systems, Power steering | Hydraulic Racks, Pumps | Safety, Enhanced control |
| Agriculture | Tractor implements | Hydraulic Cylinders, Hoses | Power, Versatility |
Fundamentals of Hydraulic Fluid Mechanics and Behavior
Understanding the fundamentals of hydraulic fluid mechanics is crucial for both beginners and experts in the field of fluid power hydraulics. At the heart of hydraulics is the behavior of fluid under pressure, which allows for the transmission of force and motion in machinery and systems. The key principles include Pascal's law, which states that pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions, and Bernoulli's principle, which explains the relationship between fluid speed and pressure. By grasping these concepts, one can appreciate how hydraulic systems efficiently convert hydraulic energy into mechanical work.
Additionally, the study of fluid behavior encompasses understanding viscosity, which affects how fluids flow and their efficiency in hydraulic systems. Fluid properties like density and temperature influence how fluids interact within a system, impacting performance and reliability. Furthermore, knowledge of hydraulic fluids, their additives, and how they behave under different temperature and pressure conditions is essential for system design and maintenance. By diving deeper into these elements of hydraulic fluid mechanics, both novices and seasoned professionals can enhance their expertise and optimize the performance of hydraulic systems in various applications.
Advanced Topics in Hydraulics for Experienced Practitioners
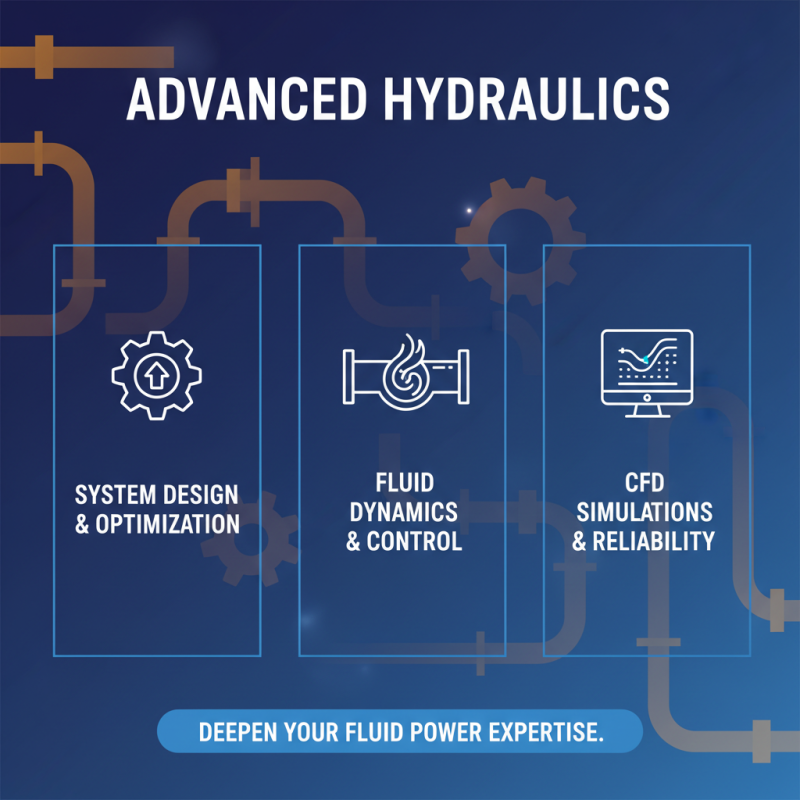
Advanced hydraulics encompasses a range of sophisticated topics that cater to experienced practitioners seeking to deepen their understanding of fluid power systems. Topics such as hydraulic system design, fluid dynamics, and advanced control methods are pivotal for optimizing performance and efficiency. Practitioners are encouraged to delve into computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations, which allow for the analysis and visualization of fluid behavior within hydraulic systems. This detailed approach not only enhances the design process but also aids in identifying potential failure points and improving system reliability.
Moreover, understanding the intricacies of hydraulic components—such as pumps, actuators, and valves—becomes crucial as one ventures into advanced applications. System integration and the configuration of hydraulic circuits require a solid grasp of both theoretical concepts and practical experience. Additionally, exploring the impact of varying fluid properties, such as viscosity and temperature, can significantly influence system performance. Experienced practitioners should also prioritize staying updated on innovations in hydraulic technologies, including renewable energy applications and smart hydraulic systems, to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving industry.
Related Posts
-
Why Fluid Power Hydraulics Are Essential for Modern Industry
-
Exploring the Future: Top Fluid Power Hydraulics Trends for 2025+
-

5 Best Fluid Power Hydraulics Solutions for Optimal Performance
-

Exploring Hydraulic Continental Solutions at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 Trends and Market Data
-

Exploring the Future of Fluid Power Hydraulics in Innovative Industries
-

Ultimate Checklist for Global Buyers in Fluid Power Procurement
 skip to Main Content
skip to Main Content
